Controllers
Installation
You can add the controllers folder on mount attribute in your server settings as follow :
import {ServerLoader, ServerSettings} from "@tsed/common";
import Path = require("path");
const rootDir = Path.resolve(__dirname);
@ServerSettings({
rootDir,
mount: {
'/rest': `${rootDir}/controllers/*.js`
}
})
export class Server extends ServerLoader {
$onMountingMiddlewares(): void|Promise<any> {
const cookieParser = require('cookie-parser'),
bodyParser = require('body-parser'),
compress = require('compression'),
methodOverride = require('method-override');
this
.use(ServerLoader.AcceptMime("application/json"))
.use(cookieParser())
.use(compress({}))
.use(methodOverride())
.use(bodyParser.json())
.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: true
}));
return null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
Versioning your API
As you have seen in the previous example, the mount attribute is an object that let you to provide the global endpoint for your all controllers under the controllers folder.
You can add more configuration to mount different endpoint associated to a folder. Here is another configuration example:
import {ServerLoader, ServerSettings} from "@tsed/common";
import Path = require("path");
@ServerSettings({
rootDir: Path.resolve(__dirname),
mount: {
"/rest": "${rootDir}/controllers/current/**/*.js",
"/rest/v1": "${rootDir}/controllers/v1/**/*.js"
}
})
export class Server extends ServerLoader {
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Decorators
Async and Promise
Ts.ED support Promise API and async instruction to send a response. Just return a promise in your method and the controller will be waiting for your promised response before sending a response to the client.
import {Controller, Get, PathParams} from "@tsed/common";
interface Calendar{
id: string;
name: string;
}
@Controller("/calendars")
export class CalendarCtrl {
@Get("/:id")
public get(
@PathParams("id") id: string
): Promise<Calendar> {
return new Promise<Calendar>((resolve: Function, reject: Function) => {
resolve({
id,
name: "test"
});
});
}
// or
@Get("/:id")
async get(
@PathParams("id") id: string
): Promise<Calendar> {
return {
id,
name: "test"
};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
Multiple routes (Alias)
Ts.ED let you define multiple routes on the same method controller, with same verb like GET or POST, or with another
verb like this:
import {Controller, Get, Post, PathParams} from "@tsed/common";
@Controller("/calendars")
export class CalendarCtrl {
@Get("/:id")
@Get("/alias/:id")
@Post("/:id/complexAlias")
async get(
@PathParams("id") id: string
): Promise<any> {
return {};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Input parameters
@PathParams decorator provide quick access to an attribute Express.request.params.
import {Controller, Get, PathParams} from "@tsed/common";
@Controller("/calendars")
export class CalendarCtrl {
@Get("/:id")
async get(
@PathParams("id") id: number
): void {
return {id: id, name: "test"}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Same decorator is available to get other params. Use BodyParams
(with the right HTTP verb @Post, @Put, etc...), QueryParams or CookiesParams
to get parameters send by the client.
HeaderParams
@HeaderParams decorator provide you a quick access to the Express.request.get()
import {Controller, Get, HeaderParams, PathParams} from "@tsed/common";
@Controller("/calendars")
export class CalendarCtrl {
@Get("/:id")
async get(
@HeaderParams("x-token") token: string,
@PathParams("id") id: number
): any {
console.log("token", token);
return {id: id};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Status
You can change the status of the response with the @Status() decorator.
import {Controller, Get, BodyParams, Status} from "@tsed/common";
interface Calendar{
id: string;
name: string;
}
@Controller("/calendars")
export class CalendarCtrl {
@Put("/")
@Status(201)
async create(
@BodyParams("name") id: string
): Promise<Calendar> {
return {
id: 2,
name: "test"
};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Response and Request
You can use a decorator to inject Express.Request, Express.Response and
Express.NextFunction services instead of the classic call provided by Express API.
Just use decorator Request (or Req), Response (or Res) and Next on your method parameters like this :
import {Controller, Get, Res, Req, Next} from "@tsed/common";
import * as Express from "express";
interface ICalendar{
id: string;
name: string;
}
@Controller("/calendars")
export class CalendarCtrl {
@Get("/:id")
get(
@Req() request: Express.Request,
@Res() response: Express.Response,
@Next() next: Express.NextFunction
): void {
setTimeout(() => {
response.send(200, {id: request.params.id, name: "test"});
next();
});
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Router
Each controller has an Express.Router instance associated with it. The ExpressRouter decorator is here to inject this instance to your controller.
import {Controller, Get, ExpressRouter} from "@tsed/common";
@Controller("/calendars")
export class CalendarCtrl {
constructor(@ExpressRouter router: ExpressRouter) {
router.get('/', this.myMethod)
}
myMethod(req, res, next){
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
In this case, injection on the method isn't available.
Custom middleware
@Use(), @UseBefore(), @UseAfter() decorators lets you add custom middleware on a method or on controller.
Example
import {Controller, Get, PathParams, Use, UseBefore, UseAfter} from "@tsed/common";
import {BadRequest} from "httpexceptions";
import {CustomMiddleware, CustomBeforeMdlw} from "../middlewares/middlewares"
@Controller("/calendars")
@UseBefore(CustomBeforeMdlw)
export class CalendarCtrl {
@Get("/:id")
@Use(CustomMiddleware)
async get(
@PathParams("id") id: number
): any {
return {id: id};
}
@Get("/:id")
@UseBefore(CustomMiddleware)
async get(
@PathParams("id") id: number
): any {
return {id: id};
}
@Get("/:id")
@UseAfter(CustomMiddleware)
async get(
@PathParams("id") id: number
): any {
return {id: id};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
For more information about the
CustomMiddlewaresee the Middlewares section.
Middleware call sequence
When a request is sent to the server all middlewares added in the ServerLoader, Controller or Endpoint with decorators will be called while a response isn't sent by one of the middleware in the stack.
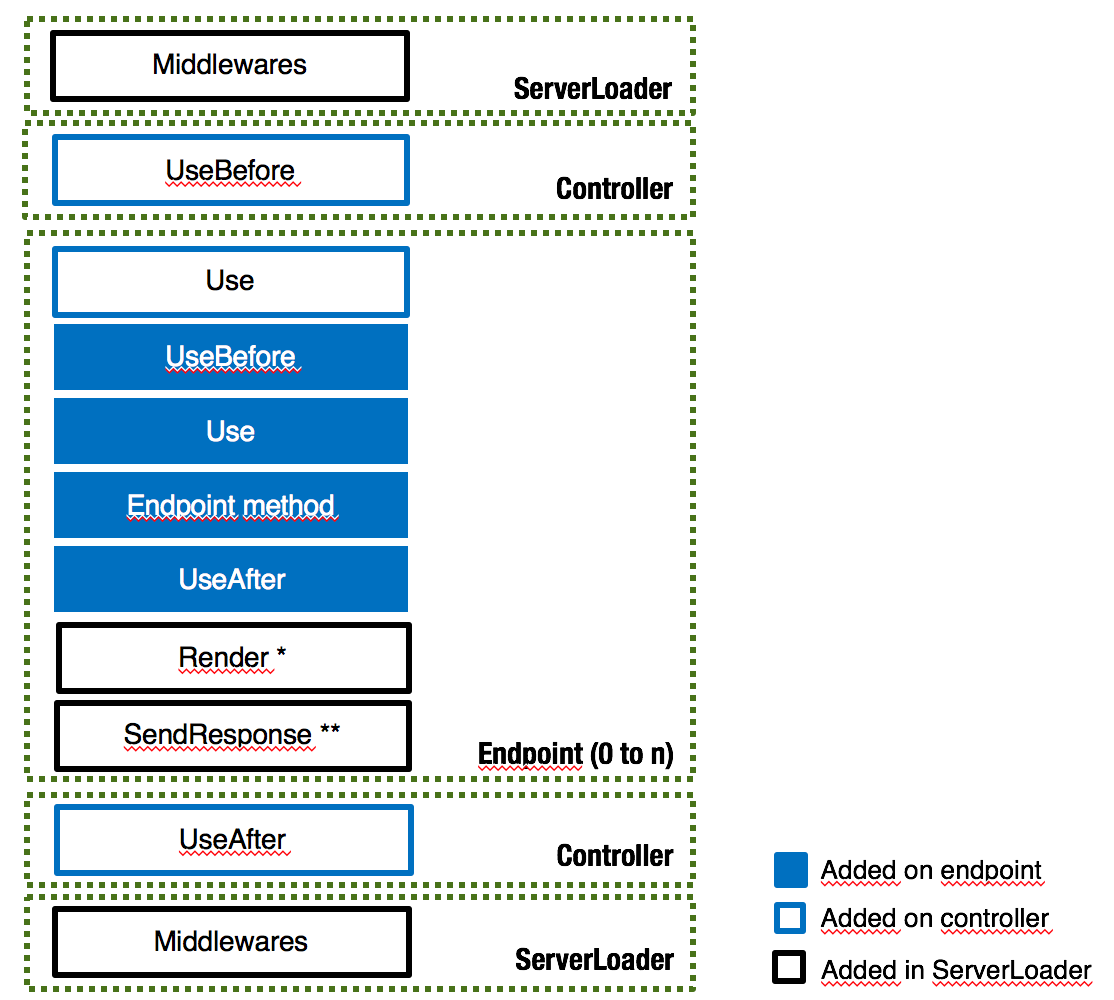
See middleware call sequence for more information.
Dependencies
A controller can depend to an other controllers. Dependencies lets you manage each Controller as Express Router module.
@Controller("/events")
export class EventCtrl {
...
}
@Controller("/calendars", EventCtrl)
export class CalendarCtrl {
...
}
@Controller("/rest")
export class RestCtrl{
constructor(
routeService: RouteService
){
console.log(routeService.printRoutes());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
In this example, CalendarCtrl have EventCtrl as dependencies. When all Controllers are built, the recorded routes will be as follows :
- /rest
- /rest/calendars
- /rest/calendars/events
Merge Params
In some case you need to have a complex routes like this rest/calendars/:calendarId/events/:eventId.
This route can be written with Ts.ED like this :
@Controller("/:calendarId/events")
class EventCtrl {
@Get("/:eventId")
async get(
@PathParams("calendarId") calendarId: string,
@PathParams("eventId") eventId: string
) {
console.log("calendarId =>", calendarId);
console.log("eventId =>", eventId);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
In this case, the calendarId will be undefined because Express.Router didn't merge params by
default from the parent Router (see Express documentation).
To solve it you can use the @MergeParams() decorator. See example:
@Controller("/:calendarId/events")
@MergeParams()
class EventCtrl {
@Get("/:eventId")
async get(
@PathParams("calendarId") calendarId: string,
@PathParams("eventId") eventId: string
) {
console.log("calendarId =>", calendarId);
console.log("eventId =>", eventId);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Now, calendarId will have the value given in the context path.
CaseSensitive and Strict options are also supported.
Inheritance
Ts.ED support the ES6 inheritance class. So you can declare a controller that implement some generic method and use it on a children class.
To do that just declare a parent controller without the @Controller decorator.
export abstract class BaseController {
constructor(private someService: SomeService) {}
@Get('/list')
async list(@QueryParams("search") search: any) {
return someService.list(search)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Then, on your children controller:
@Controller('/children')
export abstract class ChildrenCtrl extends BaseController {
@Get('/:id')
async get(@PathParams("id") id: string): Promise<any> {
return {id: id}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
Services →